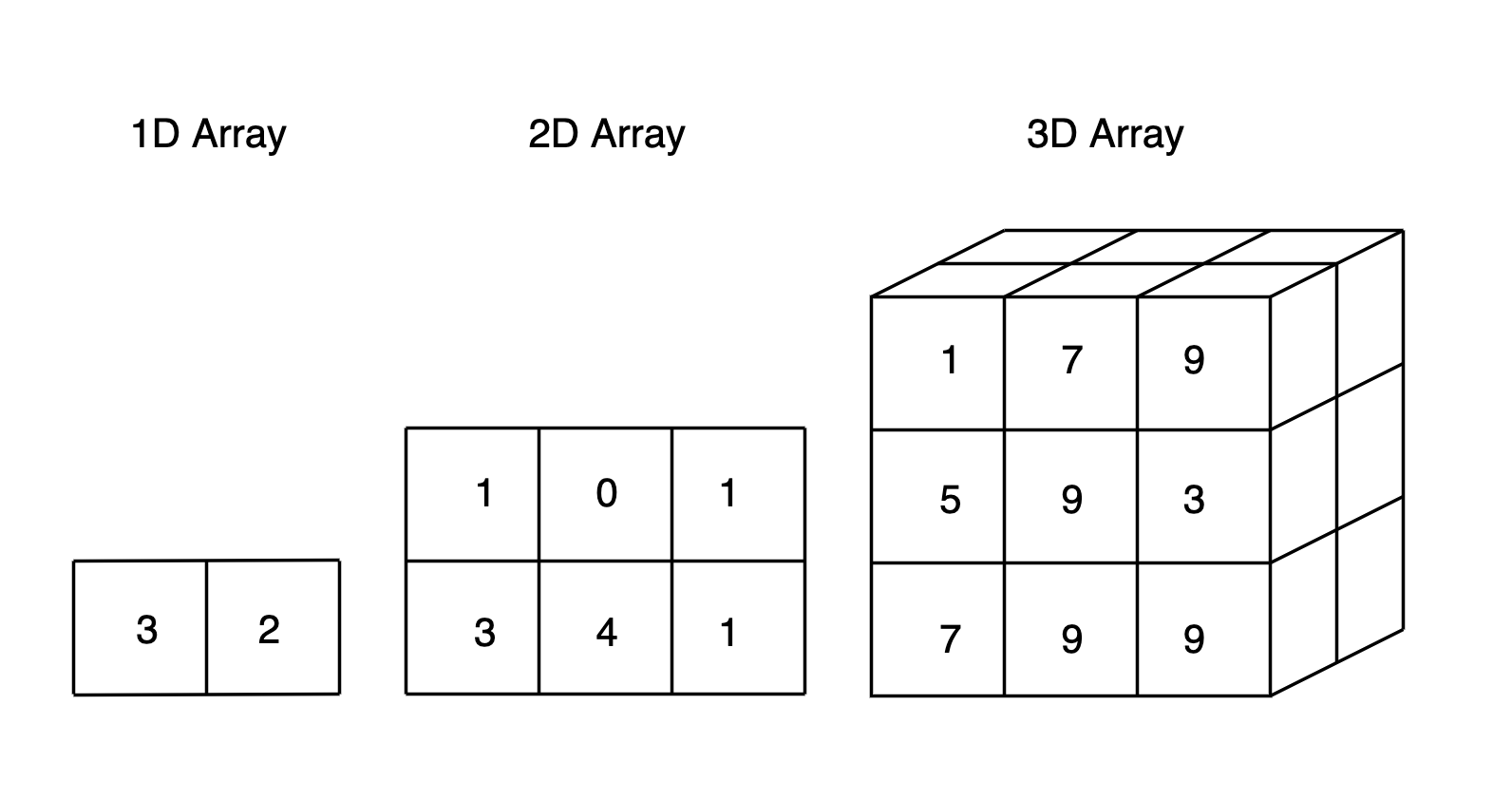
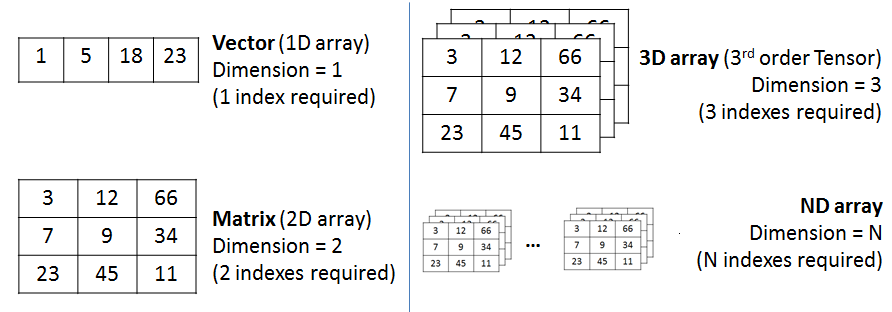
Features of an Array
- An array declaration allocates sequential memory blocks.
- Arrays are static. This means that an array once initialized cannot be resized.
- Each memory block represents an array element.
- Array elements are identified by a unique integer called as the subscript / index of the element.
- Like variables, arrays too, should be declared before they are used. Use the var keyword to declare an array.
- Array initialization refers to populating the array elements.
- Array element values can be updated or modified but cannot be deleted.
Declaring and Initializing Arrays
Syntax
var array_name[:type[]] //declaration array_name = [val1,val2,..,valn] //initialization var array_name[:type[]] = [val1,val2,…,valn]//declared and initialized
Note: default datatype in declaration is any
Example:
var array1:string[] array1 = ["t","u","t","o","r","i","a","l","s","p","o","t","s"] var array2:string[] = ["t","u","t","o","r","i","a","l","s","p","o","t","s"]
After compiling:
"use strict"; var array1; array1 = ["t", "u", "t", "o", "r", "i", "a", "l", "s", "p", "o", "t", "s"]; var array2 = ["t", "u", "t", "o", "r", "i", "a", "l", "s", "p", "o", "t", "s"];
Accessing Array Elements:
Syntax :
array_name[the_index] = value
Example:
console.log(array1[0]) console.log(array1[1])
Result:
[LOG]: t [LOG]: u
Array Object
Syntax:
Syntax 1:
var arr_name[:type[]] = new Array()
Example:
var arr_name:number[] = new Array() console.log(arr_name)
Result:
[LOG]: []
Syntax 2:
var arr_name[:type[]] = new Array(array_size)
Example:
var arr_name:number[] = new Array(4) console.log(arr_name)
Result:
[LOG]: [ null, null, null, null ]
Syntax 3:
var arr_name[:type[]] = new Array(value1,value2,...,valueN)
Example:
var arr_name:number[] = new Array(1,2,3,4) console.log(arr_name)
Result:
[LOG]: [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
Array properties:
length – dimension of array
Array Methods
| S.No. | Method & Description |
|---|---|
| 1. | concat()
Returns a new array comprised of this array joined with other array(s) and/or value(s). |
| 2. | every()
Returns true if every element in this array satisfies the provided testing function. |
| 3. | filter()
Creates a new array with all of the elements of this array for which the provided filtering function returns true. |
| 4. | forEach()
Calls a function for each element in the array. |
| 5. | indexOf()
Returns the first (least) index of an element within the array equal to the specified value, or -1 if none is found. |
| 6. | join()
Joins all elements of an array into a string. |
| 7. | lastIndexOf()
Returns the last (greatest) index of an element within the array equal to the specified value, or -1 if none is found. |
| 8. | map()
Creates a new array with the results of calling a provided function on every element in this array. |
| 9. | pop()
Removes the last element from an array and returns that element. |
| 10. | push()
Adds one or more elements to the end of an array and returns the new length of the array. |
| 11. | reduce()
Apply a function simultaneously against two values of the array (from left-to-right) as to reduce it to a single value. |
| 12. | reduceRight()
Apply a function simultaneously against two values of the array (from right-to-left) as to reduce it to a single value. |
| 13. | reverse()
Reverses the order of the elements of an array — the first becomes the last, and the last becomes the first. |
| 14. | shift()
Removes the first element from an array and returns that element. |
| 15. | slice()
Extracts a section of an array and returns a new array. |
| 16. | some()
Returns true if at least one element in this array satisfies the provided testing function. |
| 17. | sort()
Sorts the elements of an array. |
| 18. | splice()
Adds and/or removes elements from an array. |
| 19. | toString()
Returns a string representing the array and its elements. |
| 20. | unshift()
Adds one or more elements to the front of an array and returns the new length of the array. |
Array Destructuring
Syntax
var [value1,value2,...,valueN] = arr_name
Example:
var arr_name:number[] = new Array(1,2,3,4) var [value1,value2] = arr_name console.log(value1,value2)
After compiling:
"use strict"; var arr_name = new Array(1, 2, 3, 4); var value1 = arr_name[0], value2 = arr_name[1]; console.log(value1, value2);
Result:
[LOG]: 1, 2
Multi-dimensional arrays
TypeScript supports multidimensional arrays. The simplest form of the multidimensional array is the two-dimensional array (2D-array).
Example:
var arr_name:number[][] = new Array([0,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]) console.log(arr_name[0][0]) console.log(arr_name[0][1]) console.log(arr_name[0][2]) console.log(arr_name[1][0]) console.log(arr_name[1][1]) console.log(arr_name[1][2]) console.log(arr_name[2][0]) console.log(arr_name[2][1]) console.log(arr_name[2][2])
Result:
[LOG]: 0 [LOG]: 1 [LOG]: 2 [LOG]: 3 [LOG]: 4 [LOG]: 5 [LOG]: 6 [LOG]: 7 [LOG]: 8
Passing arrays to functions
You can pass to the function a pointer to an array by specifying the array’s name without an index.
Example:
var names:number[] = new Array(0,1,2,3)
function myFunc(arr_names:number[]) {
for(var i = 0;i<arr_names.length;i++) {
console.log(arr_names[i])
arr_names[i]++
}
}
myFunc(names)
console.log(names)
Result:
[LOG]: 0 [LOG]: 1 [LOG]: 2 [LOG]: 3 [LOG]: [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
Return array from functions
Allows a function to return an array
Example:
function myFunc():number[] {
return new Array(0,1,2,3)
}
var names = myFunc()
console.log(names)
Result:
[LOG]: [ 0, 1, 2, 3 ]