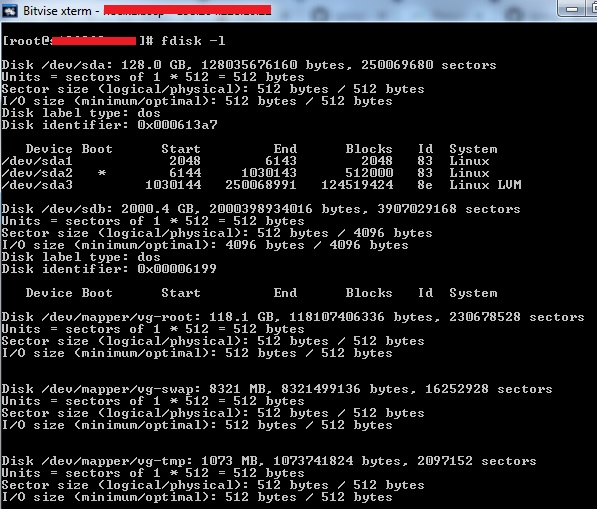
Step 1: First, list all drives on your server:
[root@tutorialspots ~]# fdisk -l Disk /dev/sda: 128.0 GB, 128035676160 bytes, 250069680 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x000613a7 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sda1 2048 6143 2048 83 Linux /dev/sda2 * 6144 1030143 512000 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1030144 250068991 124519424 8e Linux LVM Disk /dev/sdb: 2000.4 GB, 2000398934016 bytes, 3907029168 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x00006199 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System Disk /dev/mapper/vg-root: 118.1 GB, 118107406336 bytes, 230678528 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/mapper/vg-swap: 8321 MB, 8321499136 bytes, 16252928 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/mapper/vg-tmp: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
You see a big drive /dev/sdb with capacity 2T, check this drive
[root@tutorialspots ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb Disk /dev/sdb: 2000.4 GB, 2000398934016 bytes, 3907029168 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x00006199 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb is entire device, not just one partition!
Step 2: How to create a new partition in CentOS
Use command:
fdisk /dev/sdb
Then type n to create a new partition then follow this result:
[root@tutorialspots ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
The device presents a logical sector size that is smaller than
the physical sector size. Aligning to a physical sector (or optimal
I/O) size boundary is recommended, or performance may be impacted.
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-3907029167, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-3907029167, default 3907029167):
Using default value 3907029167
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 1.8 TiB is set
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
Step 3: How to format a partition in CentOS
Format new partition with type ext4
[root@tutorialspots ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
122101760 inodes, 488378390 blocks
24418919 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2636120064
14905 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616, 78675968,
102400000, 214990848
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
Now, check partitions in /dev/sdb
[root@tutorialspots ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb Disk /dev/sdb: 2000.4 GB, 2000398934016 bytes, 3907029168 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x00006199 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 3907029167 1953513560 83 Linux
Step 4: list current mounts
[root@tutorialspots ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/vg-root 109G 47G 57G 46% / devtmpfs 7.6G 0 7.6G 0% /dev tmpfs 7.7G 0 7.7G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 7.7G 619M 7.1G 8% /run tmpfs 7.7G 0 7.7G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda2 485M 157M 303M 35% /boot /dev/mapper/vg-tmp 976M 23M 887M 3% /tmp tmpfs 1.6G 0 1.6G 0% /run/user/0
Step 5: create folder you want to mount to
mkdir /mnt/store
Step 6: mount drive
mount -t ext4 /dev/sdb1 /mnt/store
Done, check
[root@tutorialspots ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/vg-root 109G 51G 53G 49% / devtmpfs 7.6G 0 7.6G 0% /dev tmpfs 7.7G 0 7.7G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 7.7G 619M 7.1G 8% /run tmpfs 7.7G 0 7.7G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda2 485M 157M 303M 35% /boot /dev/mapper/vg-tmp 976M 23M 887M 3% /tmp tmpfs 1.6G 0 1.6G 0% /run/user/0 /dev/sdb1 1.8T 77M 1.7T 1% /mnt/store
Step 7: Automatic Mount At Boot Time
Add this line to file /etc/fstab
/dev/sdb1 /mnt/store ext4 defaults 0 2
With command:
vi /etc/fstab
Some error:
Error 1:
[root@tutorialspots ~]# sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/store mount: /dev/sdb1 is write-protected, mounting read-only
Means lack file system type of drive, you must use -t flag
Error 2:
[root@tutorialspots ~]# mount -t ext3 /dev/sdb1 /mnt/store
mount: wrong fs type, bad option, bad superblock on /dev/sdb1,
missing codepage or helper program, or other error
In some cases useful info is found in syslog - try
dmesg | tail or so.
Means wrong file system type of drive, you use other file system type of drive eg: ext4